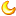In optics, particularly as relates to film and photography, the depth of field (DOF) is the distance in front of and beyond the subject that appears to be in focus. Although a lenscan precisely focus at only one distance, the decrease in sharpness isgradual on either side of the focused distance, so that within the DOF,the unsharpness is imperceptible under normal viewing conditions.
For some images, such as landscapes, a large DOF may be appropriate,while for others, such as portraits, a small DOF may be more effective.
The DOF is determined by the subject distance, the lens focal length, and the lens f-number (relative aperture). Except at close-up distances, DOF is approximately determined by the subject magnification and the lens f-number. For a given f-number,increasing the magnification, either by moving closer to the subject orusing a lens of greater focal length, decreases the DOF; decreasingmagnification increases DOF. For a given subject magnification,increasing the f-number (decreasing the relative aperture) increases the DOF; decreasing f-number decreases DOF.
When focus is set to the hyperfocal distance, the DOF extends from half the hyperfocal distance to infinity, and is the largest DOF possible for a given f-number.
The advent of digital technology in photography has providedadditional means of controlling the extent of image sharpness; somemethods allow DOF that would be impossible with traditional techniques,and some allow the DOF to be determined after the image is made.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Depth_of_field |